Cabling Infrastructure: The Benefits of Structured Cabling Systems
In today's digital age, businesses rely heavily on efficient and reliable communication networks.
Created by: Daniel Ogunsemowo /
Vetted by:
Otse Amorighoye
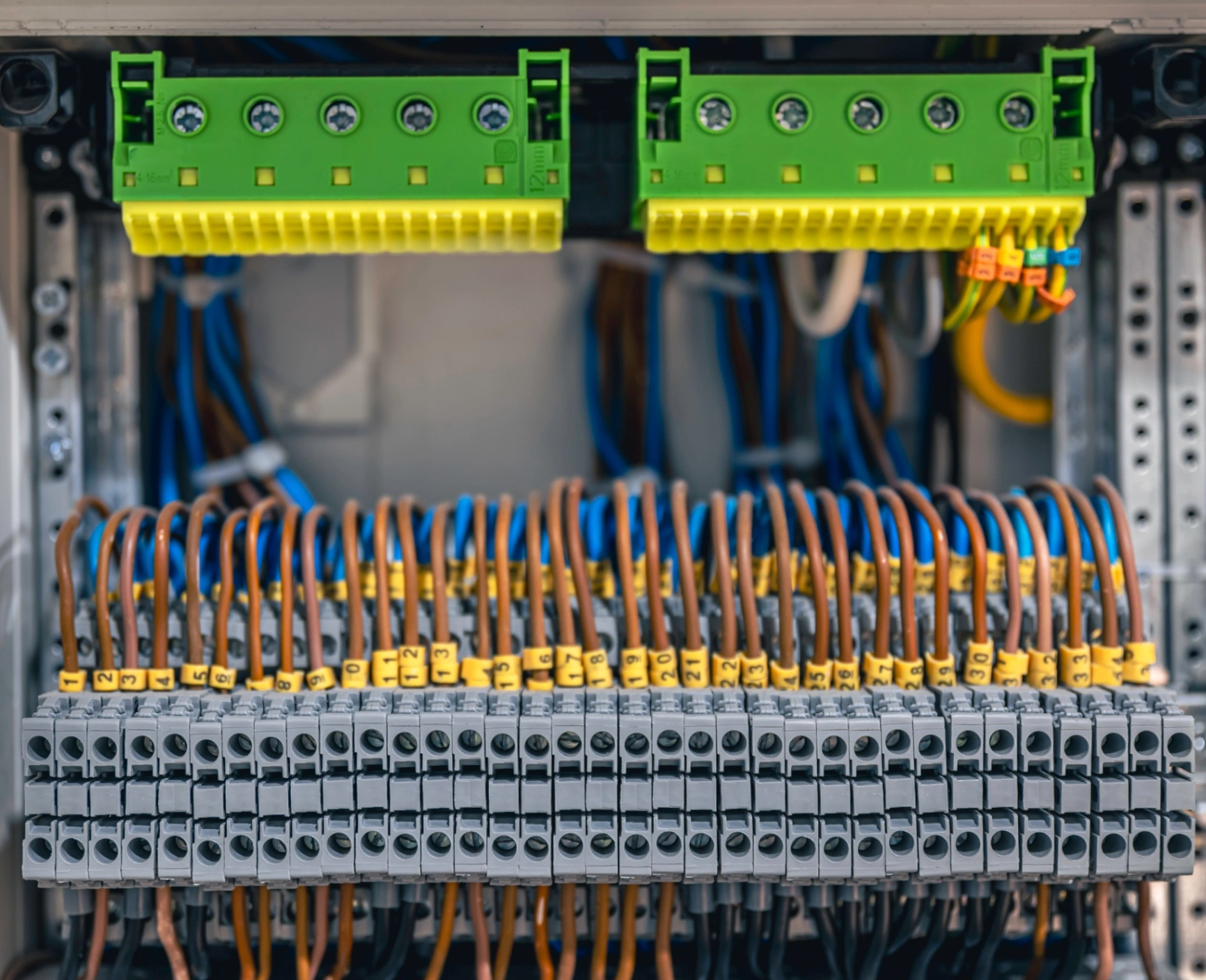
In today's digital age, businesses rely heavily on efficient and reliable communication networks. Structured cabling systems form the backbone of these networks, enabling seamless connectivity and supporting various technological advancements. This article explores the numerous benefits of structured cabling systems and emphasizes their importance in future-proofing your cabling infrastructure.
Introduction to Structured Cabling Systems
Structured cabling is a standardized approach to designing and installing a cabling system that can support multiple hardware uses and be suitable for today's needs and those of the future. Unlike traditional point-to-point cabling, structured cabling follows a methodical design, ensuring all hardware and cabling meet performance standards. To learn more about what structured cabling systems entail, refer to Decoding What Is a Structured Cabling System: A Comprehensive Guide.
The Importance of Structured Cabling Infrastructure
1. Enhanced Network Performance
Structured cabling systems significantly enhance network performance by reducing latency and minimizing signal interference. This leads to faster data transfer speeds, improved communication, and increased productivity. For tips on improving network performance, you might find Steps for Data Network Cabling Installation helpful.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the key benefits of structured cabling is its scalability. Businesses can easily expand their network infrastructure without disrupting existing operations. The modular design allows for the integration of new devices and applications, ensuring long-term flexibility.
3. Simplified Management
Structured cabling systems simplify network management by organizing cables into a single, unified infrastructure. This makes it easier to identify and resolve issues, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For more on maintenance and troubleshooting, visit Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Data Network Cables.
4. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in structured cabling may be higher than traditional cabling, the long-term cost savings are substantial. Reduced maintenance, lower downtime, and efficient management contribute to overall cost efficiency.
5. Future-Proofing Technology
Structured cabling systems are designed to support future technological advancements. As businesses adopt new technologies like IoT, 5G, and cloud computing, structured cabling ensures seamless integration and optimal performance. For insights into future-proofing, see Future-Proofing Your Infrastructure: The Benefits of Structured Cabling Systems.
Components of Structured Cabling Infrastructure
1. Horizontal Cabling
Horizontal cabling connects telecommunications rooms to individual outlets or work areas. It typically consists of twisted-pair copper cables or fiber optic cables, ensuring reliable and high-speed connections.
2. Vertical Cabling (Backbone Cabling)
Vertical cabling, also known as backbone cabling, connects different telecommunications rooms within a building or campus. This includes the main distribution area, intermediate distribution areas, and horizontal cross-connects.
3. Telecommunications Room
The telecommunications room houses networking equipment, patch panels, and other essential hardware. It acts as the central hub for all cabling connections, facilitating efficient management and troubleshooting.
4. Work Area Components
Work area components include the outlets, patch cords, and devices connected to the network. These components ensure that end-users have reliable access to the network and can easily connect and disconnect devices as needed.
5. Consolidation Points
Consolidation points are intermediate connection points that facilitate easier changes and moves within the network. They are particularly useful in environments with frequent layout changes, such as open office spaces.
Benefits of Structured Cabling in Different Sectors
1. Corporate Offices
Structured cabling is essential in corporate offices to support various communication systems, including voice, data, and video conferencing. It ensures reliable connectivity, enhances productivity, and allows for seamless integration of new technologies. For more information, check out Benefits of Structured Cabling.
2. Healthcare Facilities
In healthcare, reliable and efficient communication networks are crucial for patient care. Structured cabling supports the integration of electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, and other medical technologies, ensuring accurate and timely information sharing.
3. Educational Institutions
Educational institutions rely on structured cabling to support computer labs, multimedia classrooms, and campus-wide networks. It provides the bandwidth needed for online learning platforms, research, and administrative functions.
4. Data Centers
Data centers are the backbone of modern business operations. Structured cabling ensures high-speed data transfer, reduces latency, and supports the growing demands of cloud computing and big data analytics. For best practices, refer to Best Practices for Structured Cabling Design.
5. Industrial Environments
In industrial environments, structured cabling supports automation, machine-to-machine communication, and IoT applications. It ensures reliable and secure data transfer in harsh conditions, improving operational efficiency.
Designing and Implementing Structured Cabling Systems
1. Assessing Requirements
The first step in designing a structured cabling system is to assess the specific needs of the organization. This includes understanding the current and future network requirements, the number of devices, and the types of applications being used.
2. Planning and Layout
Effective planning and layout are crucial for the success of a structured cabling system. This involves designing the cabling pathways, selecting appropriate cabling types, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
3. Cable Management
Proper cable management is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of the network. This includes organizing cables, labeling connections, and using cable management tools like racks, trays, and conduits. For tips on cable management, see Ethernet Cable Management Tips.
4. Installation
Professional installation is critical for the success of a structured cabling system. Certified technicians should follow industry best practices and standards to ensure proper termination, testing, and documentation of the cabling system.
5. Testing and Certification
After installation, the cabling system should be thoroughly tested and certified to ensure it meets performance standards. This includes testing for continuity, signal loss, and interference.
6. Documentation and Maintenance
Comprehensive documentation is essential for the long-term management of a structured cabling system. This includes detailed records of cable routes, connections, and test results. Regular maintenance and inspections help identify and resolve issues before they impact network performance.
Future Trends in Structured Cabling
1. Increased Adoption of Fiber Optics
Fiber optic cabling offers superior performance, higher bandwidth, and longer transmission distances compared to traditional copper cabling. As data demands increase, more organizations are adopting fiber optics for their structured cabling systems. To understand the benefits, read Advantages of Using Fiber Optic Cabling for a Network.
2. Growth of IoT and Smart Buildings
The Internet of Things (IoT) and smart building technologies are driving the need for robust and scalable cabling infrastructure. Structured cabling systems provide the foundation for these technologies, enabling seamless connectivity and data transfer.
3. 5G Integration
The rollout of 5G networks is revolutionizing communication and connectivity. Structured cabling systems play a crucial role in supporting 5G infrastructure, ensuring high-speed data transfer and low latency.
4. Sustainability and Green Cabling
Environmental concerns are prompting organizations to adopt sustainable practices in their cabling infrastructure. This includes using eco-friendly materials, reducing energy consumption, and recycling old cables.
5. Enhanced Security
With the growing threat of cyberattacks, security is a top priority for organizations. Structured cabling systems support advanced security measures, including encryption, monitoring, and access control, to protect sensitive data.
Case Studies
1. Corporate Office Transformation
A multinational corporation upgraded its network infrastructure with a structured cabling system to support its growing workforce and technological needs. The new system enhanced network performance, reduced downtime, and provided the flexibility to accommodate future growth. For more on structured cabling in corporate environments, see Office Data Cabling: The Ultimate Guide to Efficient and Reliable Network Infrastructure.
2. Hospital Network Upgrade
A large hospital implemented a structured cabling system to support its electronic health records (EHR) and telemedicine initiatives. The system improved data transfer speeds, ensured reliable connectivity, and enhanced patient care.
3. University Campus Expansion
A university expanded its campus network with a structured cabling system to support online learning, research, and administrative functions. The system provided the necessary bandwidth, reduced latency, and facilitated seamless integration of new technologies.
4. Data Center Optimization
A data center upgraded its cabling infrastructure to meet the demands of cloud computing and big data analytics. The structured cabling system improved data transfer speeds, reduced latency, and supported future technological advancements.
Best Practices for Structured Cabling
1. Follow Industry Standards
Adhering to industry standards, such as ANSI/TIA-568 and ISO/IEC 11801, ensures the structured cabling system meets performance and reliability requirements.
2. Plan for Future Growth
Design the cabling infrastructure with future growth in mind. This includes considering the scalability of the system, selecting appropriate cabling types, and allowing for the integration of new technologies.
3. Implement Proper Cable Management
Proper cable management is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of the network. This includes organizing cables, labeling connections, and using cable management tools.
4. Regular Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing and maintenance help identify and resolve issues before they impact network performance. This includes testing for continuity, signal loss, and interference.
5. Comprehensive Documentation
Maintain comprehensive documentation of the cabling system, including cable routes, connections, and test results. This facilitates easier troubleshooting and management of the network.
Conclusion
Structured cabling systems are essential for future-proofing your infrastructure and ensuring reliable and efficient communication networks. They offer numerous benefits, including enhanced network performance, scalability, simplified management, cost efficiency, and support for future technological advancements. By following best practices and staying abreast of industry trends, organizations can optimize their cabling infrastructure and stay ahead in the digital age.
Structured cabling is not just a necessity but an investment in the future of your business. It provides the backbone for all your communication needs, ensuring that your network is robust, flexible, and ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Whether you're a small business, a large corporation, or a public institution, structured cabling can transform your operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth. By embracing structured cabling, you're not only addressing your current needs but also preparing for the future. As technology continues to evolve, having a solid and adaptable cabling infrastructure will be a critical factor in your success. Whether you're looking to upgrade your existing network or build a new one from the ground up, structured cabling offers the reliability, performance, and scalability you need to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital world.
FAQ Section
What is structured cabling?
Structured cabling is a standardized approach to designing and installing a cabling system that supports multiple hardware uses, ensuring reliability, scalability, and future-proofing. For more details, read What is Structured Cabling?.
Why is structured cabling important?
Structured cabling enhances network performance, simplifies management, reduces costs, and supports future technological advancements, making it essential for reliable and efficient communication networks. For further reading, see Understanding Structured Cabling.
What components are included in a structured cabling system?
A structured cabling system includes horizontal cabling, vertical cabling (backbone cabling), telecommunications rooms, work area components, and consolidation points.
How does structured cabling benefit different sectors?
Structured cabling benefits various sectors, including corporate offices, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, data centers, and industrial environments, by ensuring reliable connectivity and supporting advanced technologies.
What are some future trends in structured cabling?
Future trends in structured cabling include increased adoption of fiber optics, growth of IoT and smart buildings, 5G integration, sustainability, and enhanced security measures
What is structured cabling?
Structured cabling is a standardized approach to designing and installing a cabling system that supports multiple hardware uses, ensuring reliability, scalability, and future-proofing. For more details, read What is Structured Cabling?.
Why is structured cabling important?
Structured cabling enhances network performance, simplifies management, reduces costs, and supports future technological advancements, making it essential for reliable and efficient communication networks. For further reading, see Understanding Structured Cabling.
What components are included in a structured cabling system?
A structured cabling system includes horizontal cabling, vertical cabling (backbone cabling), telecommunications rooms, work area components, and consolidation points.
How does structured cabling benefit different sectors?
Structured cabling benefits various sectors, including corporate offices, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, data centers, and industrial environments, by ensuring reliable connectivity and supporting advanced technologies.
What are some future trends in structured cabling?
Future trends in structured cabling include increased adoption of fiber optics, growth of IoT and smart buildings, 5G integration, sustainability, and enhanced security measures